Monocyte mediator
Gammaherpesviruses (γHVs) coevolved with their hosts in a manner that allows for the lifelong persistence of these viruses in immunocompetent individuals. The presence of latent γHVs in host organisms has been shown to shape adaptive immunity, and here, Maquet et al. observed that pulmonary infection of mice with a murine γHV (MuHV-4) leads to recruitment of Ly6Chi monocytes (MOs) to airways. These γHV-imprinted Ly6Chi MOs recruit CD4 T cells to airways followed by engagement of the immunosuppressive PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway, which limits pathological cytotoxic CD4 T cell responses. These findings highlight a role for γHV-imprinted Ly6Chi MOs in shaping CD4 T cell functions and suggest a potential pathway for the development of therapeutics that target respiratory viral infections.
Abstract
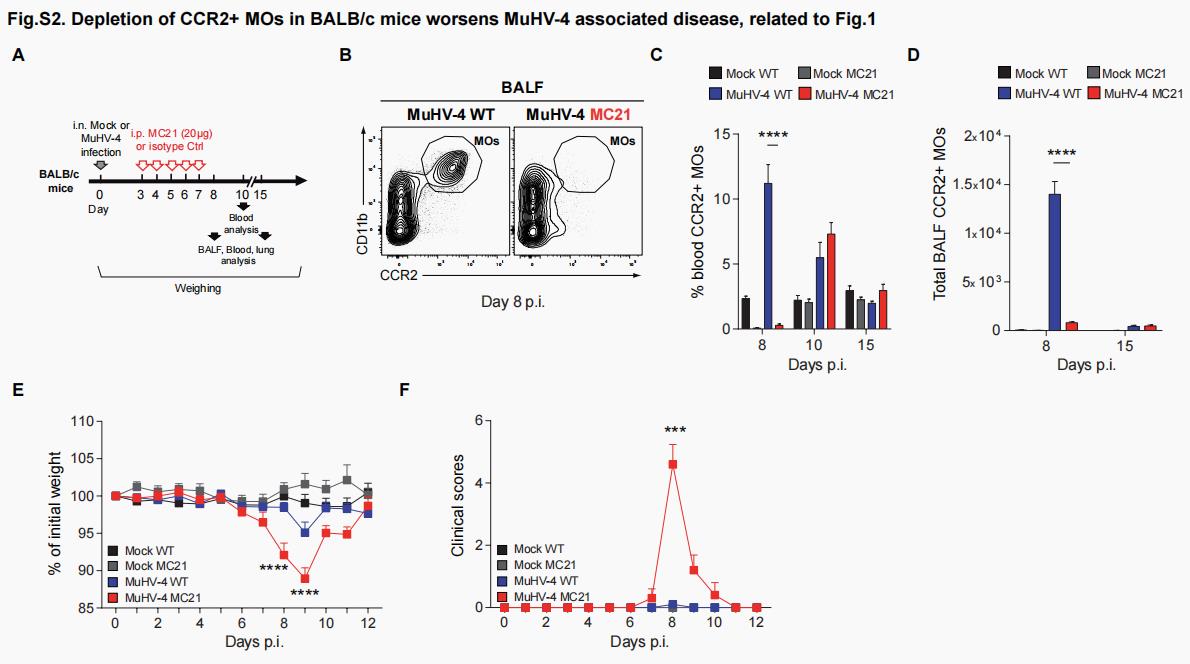
Gammaherpesviruses (γHVs) have coevolved with their host, leading to a remarkably high infection prevalence and establishment of latency. The lifelong persistence of γHVs in hosts appears to broadly shape host immunity, and we show here that pulmonary infection with Murid herpesvirus 4 (MuHV-4), a mouse γHV, drives the recruitment of Ly6Chi monocytes (MOs) into the airway, thereby modulating the host immune response. The absence of Ly6Chi MOs is associated with severe virus-induced immunopathology and the systemic release of inflammatory mediators. Mechanistically, MuHV-4–imprinted MOs recruit CD4 T cells to the airways and trigger immunosuppressive signaling pathways through the PD-L1/PD-1 axis, thereby dampening the deleterious activation of cytotoxic CD4 T cells. These results uncover a role for Ly6Chi MOs in modulating CD4 T cell functions and reveal pathways that could be targeted therapeutically to reduce detrimental immunopathological responses associated with respiratory viral infections.
Disclaimer:
Partial content of this page is transferred from the network, only for the use of scientific communication, if there is infringement, please contact us to delete. See the Privacy Policy for more information.