Keeping Tregs stable
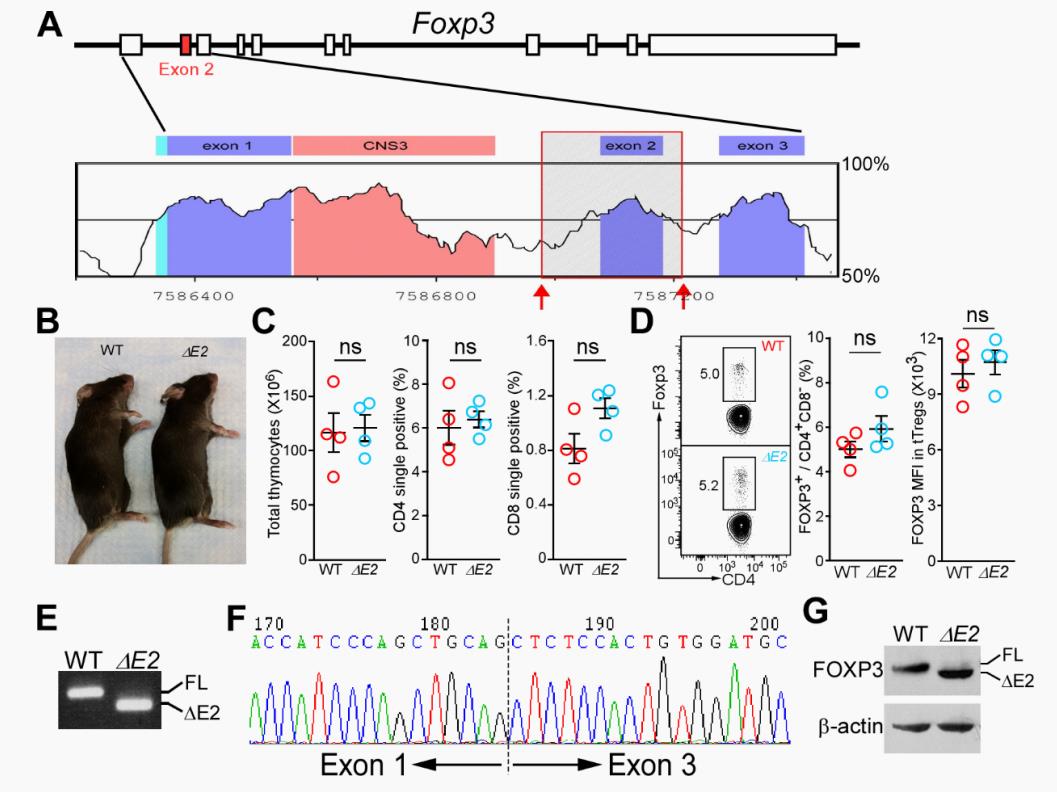
Human FOXP3 encodes two major isoforms regulated by alternative splicing: a full-length isoform and an isoform lacking exon 2 (FOXP3 ΔE2). How these isoforms differ in regulating Treg function is not well understood. Du et al. generated a mouse model in which Tregs express only FOXP3 ΔE2 and identified that these mice developed systemic autoimmunity featuring anti-dsDNA autoantibodies and immune complex glomerulonephritis, caused by exacerbated TFH and germinal center responses. Expression of the FOXP3 ΔE2 isoform resulted in Treg instability, increased expression of inflammatory cytokines, and down-regulation of positive regulators of Foxp3. Furthermore, human patients who expressed only the FOXP3 ΔE2 isoform developed immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked (IPEX) syndrome. These results identify FOXP3 exon 2 as a critical regulator of Treg function.
Abstract
Differing from the mouse Foxp3 gene that encodes only one protein product, human FOXP3 encodes two major isoforms through alternative splicing—a longer isoform (FOXP3 FL) containing all the coding exons and a shorter isoform lacking the amino acids encoded by exon 2 (FOXP3 ΔE2). The two isoforms are naturally expressed in humans, yet their differences in controlling regulatory T cell phenotype and functionality remain unclear. In this study, we show that patients expressing only the shorter isoform fail to maintain self-tolerance and develop immunodeficiency, polyendocrinopathy, and enteropathy X-linked (IPEX) syndrome. Mice with Foxp3 exon 2 deletion have excessive follicular helper T (TFH) and germinal center B (GC B) cell responses, and develop systemic autoimmune disease with anti-dsDNA and antinuclear autoantibody production, as well as immune complex glomerulonephritis. Despite having normal suppressive function in in vitro assays, regulatory T cells expressing FOXP3 ΔE2 are unstable and sufficient to induce autoimmunity when transferred into Tcrb-deficient mice. Mechanistically, the FOXP3 ΔE2 isoform allows increased expression of selected cytokines, but decreased expression of a set of positive regulators of Foxp3 without altered binding to these gene loci. These findings uncover indispensable functions of the FOXP3 exon 2 region, highlighting a role in regulating a transcriptional program that maintains Treg stability and immune homeostasis.
sources:SCIENCE IMMUNOLOGY, 24 Jun 2022, Vol 7, Issue 72,
DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abo5407
Disclaimer:
Partial content of this page is transferred from the network, only for the use of scientific communication, if there is infringement, please contact us to delete. See the Privacy Policy for more information.