A central role for STAT5 in the transcriptional programing of T helper cell metabolism
Activation answers
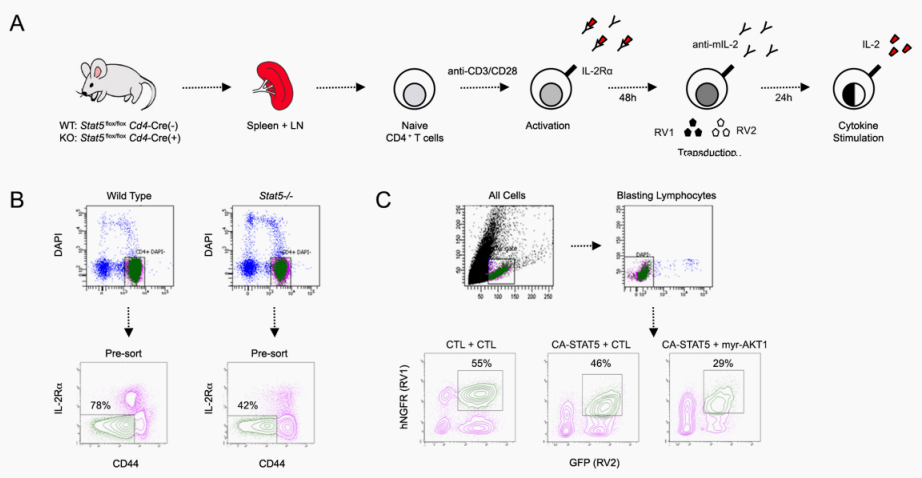
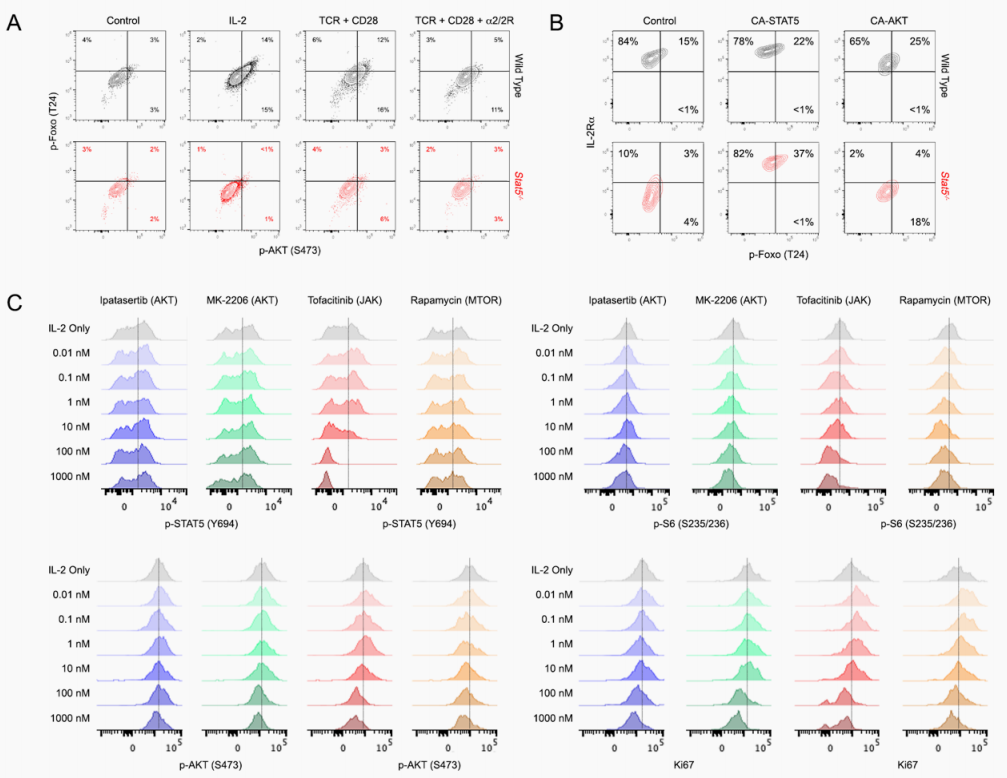
T cell activation requires changes in metabolism needed for the energy demands of rapid growth and proliferation. Cytokines that engage common gamma chain (cγ) receptors on T cells are critical to promoting metabolic changes needed for activation, and here, Villarino et al. examine the role of STAT5 engagement, which is a signaling pathway shared by all cγ cytokines. STAT5 was defined as a master regulator of amino acid metabolism in CD4+ T helper cells through interactions with enhancers and promoters of genes encoding a wide array of enzymes and transporters. STAT5 controlled transcription of members of the mTOR pathway to license T cells for IL-2–mediated mTOR signaling and promoted MYC-driven metabolic changes. Together, these findings provide molecular insights downstream of IL-2 engagement that are critical to T cell activation. – CNF.
Abstract
Activated lymphocytes adapt their metabolism to meet the energetic and biosynthetic demands imposed by rapid growth and proliferation. Common gamma chain (cγ) family cytokines are central to these processes, but the role of downstream signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) signaling, which is engaged by all cγ members, is poorly understood. Using genome-, transcriptome-, and metabolome-wide analyses, we demonstrate that STAT5 is a master regulator of energy and amino acid metabolism in CD4+ T helper cells. Mechanistically, STAT5 localizes to an array of enhancers and promoters for genes encoding essential enzymes and transporters, where it facilitates p300 recruitment and epigenetic remodeling. We also find that STAT5 licenses the activity of two other key metabolic regulators, the mTOR signaling pathway and the MYC transcription factor. Building on the latter, we present evidence for transcriptome-wide cooperation between STAT5 and MYC in both normal and transformed T cells. Together, our data provide a molecular framework for transcriptional programing of T cell metabolism downstream of cγ cytokines and highlight the JAK-STAT pathway in mediating cellular growth and proliferation.
Author information: ALEJANDRO V. VILLARINO, ARIAN DJ LAURENCE, FRED P. DAVIS, LUIS NIVELO, STEPHEN R. BROOKS, HONG-WEI SUN, KAN JIANG, BEHDAD AFZALI, DANIELA FRASCA, LOTHAR HENNIGHAUSEN, YUKA KANNO , AND JOHN J. O’SHEA
For More information, please visit: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciimmunol.abl9467
Sources: SCIENCE IMMUNOLOGY,,Vol 7, Issue 77
Published: 25 Nov 2022
DOI:10.1126/sciimmunol.abl9467
Disclaimer:
Partial content of this page is transferred from the network, only for the use of scientific communication, if there is infringement, please contact us to delete. See the Privacy Policy for more information.